Plastic injection moulding is one of the widely used manufacturing processes for producing plastic parts, ranging from small components to large, intricate products. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mould, where it cools and solidifies to form the desired shape. The quality, precision, and efficiency of this process are largely dependent on the materials used to create the plastic injection mould.

Overview of Plastic Injection Moulding
Plastic injection moulding is a highly efficient process used for mass production of plastic parts. The process involves melting plastic pellets and injecting the molten plastic into a mould cavity under high pressure. The plastic then cools and solidifies in the mould, taking the shape of the cavity. The material composition of the mould is critical to the success of the process, as it must withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved, while also ensuring the precision and durability of the moulded parts.
Materials Used in Plastic Injection Moulds
The material composition of a plastic injection mould refers to the specific types of metals and alloys that are used to fabricate the mould. The materials selected for mould construction must possess certain key properties, such as strength, hardness, heat resistance, and machinability. The commonly used materials for plastic injection moulds include steel, aluminum, and various alloy combinations.
Steel: The Common Material
Steel is by far the commonly used material in the construction of plastic injection moulds. It is preferred for its durability, strength, and ability to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the injection moulding process. Steel moulds are often used for high-volume production runs due to their long lifespan and resistance to wear.
High Carbon Steel: High carbon steel, also known as tool steel, is a popular choice for injection moulds. It has a high carbon content, which gives it increased hardness and wear resistance. High carbon steel is typically used for moulds that will be subjected to high levels of stress and abrasion.
Alloy Steel: Alloy steels, which contain additional elements such as chromium, molybdenum, or vanadium, are commonly used for plastic injection moulds. These alloys provide improved toughness, resistance to corrosion, and better thermal stability. Alloy steel moulds are ideal for applications where the mould will be exposed to unusual temperatures or aggressive plastic materials.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is another option for mould construction. It is highly resistant to corrosion, making it a good choice for producing parts that require high chemical resistance. However, stainless steel is generally more expensive and harder to machine than other types of steel.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Aluminum is another material often used for plastic injection moulds, particularly for short production runs or low-volume manufacturing. Aluminum is lighter and easier to machine compared to steel, making it a more cost-effective option for certain applications. While it may not be as durable as steel, aluminum is suitable for lower-volume production or prototype development where speed and cost are more important than the longevity of the mould.
Aluminum Alloys: Various aluminum alloys, such as 7075 and 6061, are used in mould construction. These alloys offer a balance between strength, machinability, and thermal conductivity. Aluminum moulds are particularly useful for manufacturing parts that require fast cycle times or are made from low-viscosity plastic materials.
Thermal Conductivity: One of the key advantages of aluminum is its thermal conductivity. This allows for faster cooling of the injected plastic, reducing cycle times and improving overall production efficiency. However, aluminum moulds are generally less durable than steel moulds and may be prone to wear over extended use.

Mold material: S136H 、718H、NAK80、 P20、2738、8407、SKD61、H13Mould cavity number: single cavity, multi cavityProcessing accuracy: 0.05mmMold

We have ISO9001 international quality management system and experience in controlling production costs in China. Therefore, we can help you save 20% -

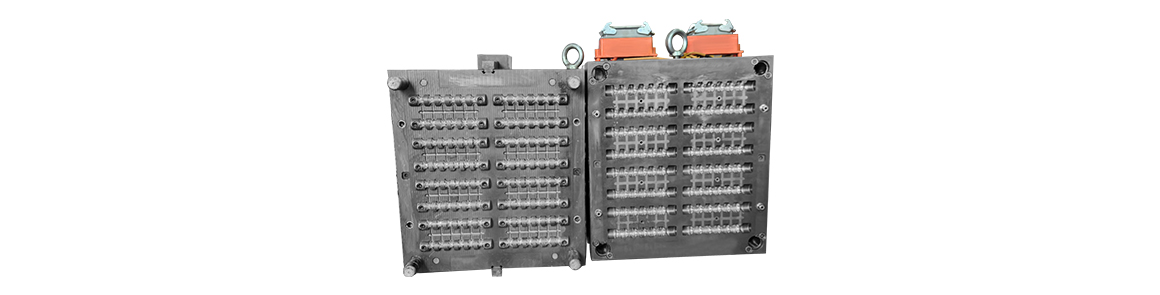
Mold material: S136 HRC48-52Manufacturing process: CNC milling, CNC machining, EDM/wire cuttingWe are equipped with the world's top precision machinin
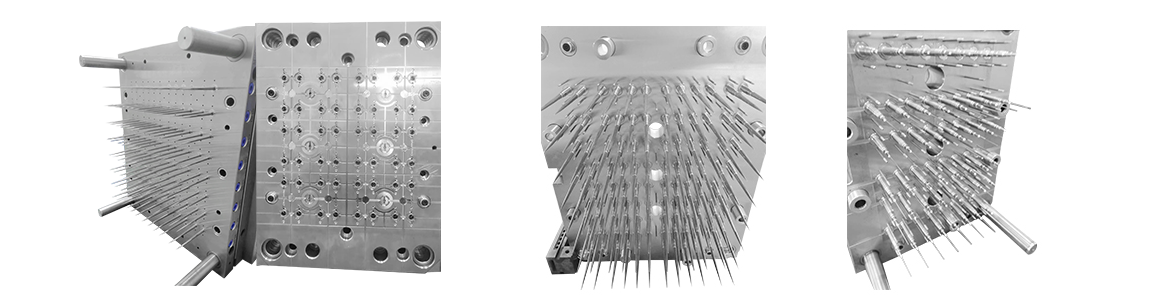
Our liquid transfer gun suction head medicine mould is made of high-quality materials as a whole. There are no burrs at the tip and mouth of the produ

The mold has a short injection cycle, high efficiency, long life, and low cost. Adopting the special flow channel design of the international advanced
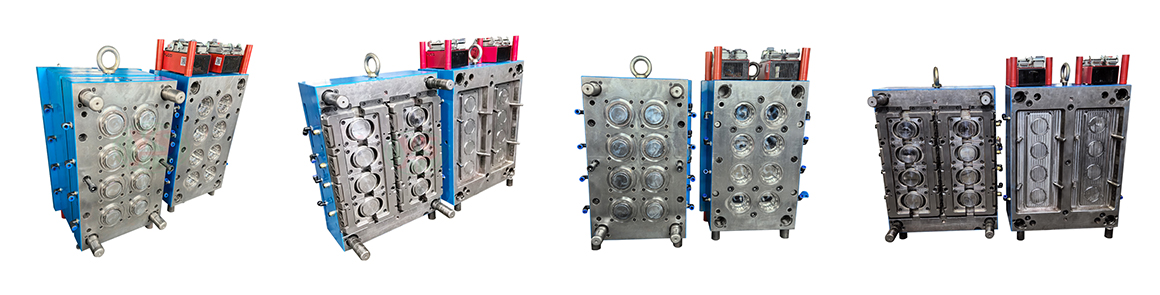
This type of mould is assembled from outer cap and an inner anti-theft ring. The outer cap is automatically rotated and pushed out by a hydraulic moto