There are many factors that affect the cooling of the injection mold, such as the shape of the plastic part and the design of the parting surface, the type, temperature, flow rate of the cooling medium, the geometric parameters and spatial arrangement of the cooling pipe, the mold material, the melt temperature, and the top required by the plastic part. The output temperature and mold temperature, the thermal cycle interaction between the plastic part and the mold, etc.
Low mold temperature can reduce the molding shrinkage of plastic parts.
Uniform mold temperature, short cooling time, and fast injection speed can reduce the warpage of plastic parts.
For crystalline polymers, increasing the mold temperature can stabilize the size of the plastic part and avoid post-crystallization, but it will lead to the defects of prolonged molding cycle and brittle plastic parts.
As the crystallinity of the crystalline polymer increases, the stress crack resistance of the plastic decreases, so it is advantageous to lower the mold temperature. However, for high-viscosity amorphous polymers, due to their resistance to cracking is directly related to the internal stress of the plastic part, it is advantageous to increase the mold temperature and filling speed and reduce the refilling time.
Increasing the mold temperature can improve the surface quality of the plastic parts. Determination of the mold temperature During the injection molding process, the mold temperature directly affects the filling of the plastic, the shaping of the plastic part, the molding cycle and the quality of the plastic part.
The mold temperature depends on the crystallinity of the plastic, the size and structure of the plastic part, performance requirements, and other process conditions such as melt temperature, injection speed, injection pressure, and molding cycle.
For amorphous polymers, the melt solidifies as the temperature decreases after being injected into the mold cavity, but no phase transition occurs. The mold temperature mainly affects the viscosity of the melt, that is, the mold filling rate. Therefore, for amorphous plastics with low and medium melt viscosity, such as polystyrene, cellulose acetate, etc., using a lower mold temperature can shorten the cooling time.

Mold material: S136H 、718H、NAK80、 P20、2738、8407、SKD61、H13Mould cavity number: single cavity, multi cavityProcessing accuracy: 0.05mmMold

We have ISO9001 international quality management system and experience in controlling production costs in China. Therefore, we can help you save 20% -

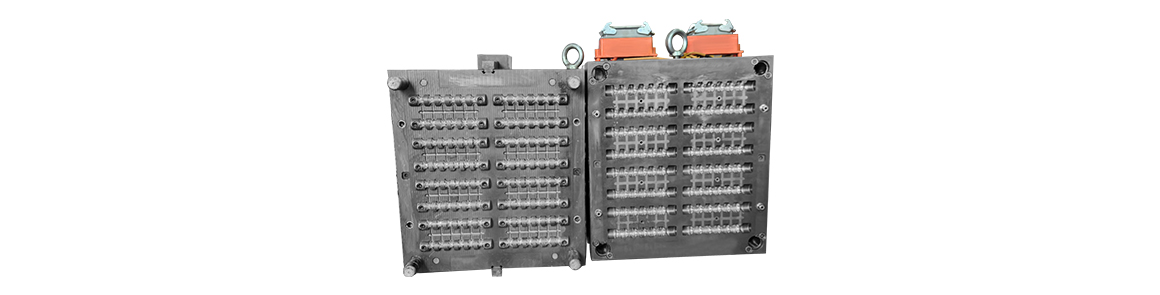
Mold material: S136 HRC48-52Manufacturing process: CNC milling, CNC machining, EDM/wire cuttingWe are equipped with the world's top precision machinin
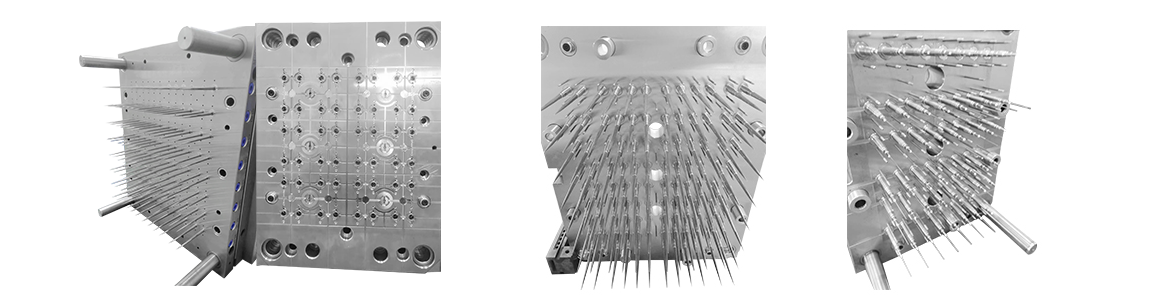
Our liquid transfer gun suction head medicine mould is made of high-quality materials as a whole. There are no burrs at the tip and mouth of the produ

The mold has a short injection cycle, high efficiency, long life, and low cost. Adopting the special flow channel design of the international advanced
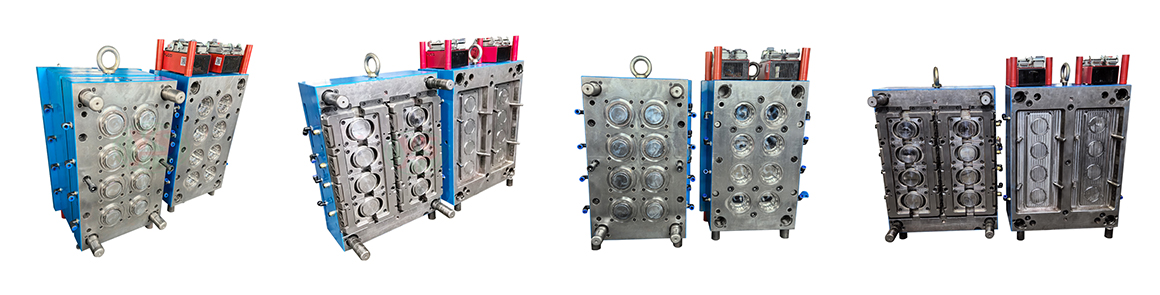
This type of mould is assembled from outer cap and an inner anti-theft ring. The outer cap is automatically rotated and pushed out by a hydraulic moto